Get paid what you deserve a step by step guide to the air force nh pay scale – Get Paid What You Deserve: A Step-by-Step Guide to the Air Force NH Pay Scale delves into the complexities of military compensation. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the Air Force pay system, outlining base pay, special allowances, and factors influencing salary. We’ll explore how years of service, rank, location, and special qualifications impact earnings, offering a clear understanding of potential income and career progression.
From understanding the basic structure of the Air Force pay system and its various components to comparing military salaries with civilian counterparts, this guide equips readers with the knowledge to make informed decisions about their Air Force career. We’ll examine the impact of promotions, additional benefits, and the Air Force retirement system, offering a holistic view of total compensation.
Understanding the Air Force Pay System
The Air Force compensation system is multifaceted, comprising base pay, special pays, and allowances. Understanding its structure is crucial for accurately assessing potential earnings.
Air Force Pay Grades and Base Pay
The Air Force utilizes a pay grade system, ranging from E-1 (Airman Basic) to O-10 (Chief Master Sergeant of the Air Force). Each grade corresponds to a specific base pay, determined by years of service. Base pay forms the foundation of an Airman’s total compensation.
Special Pays and Allowances
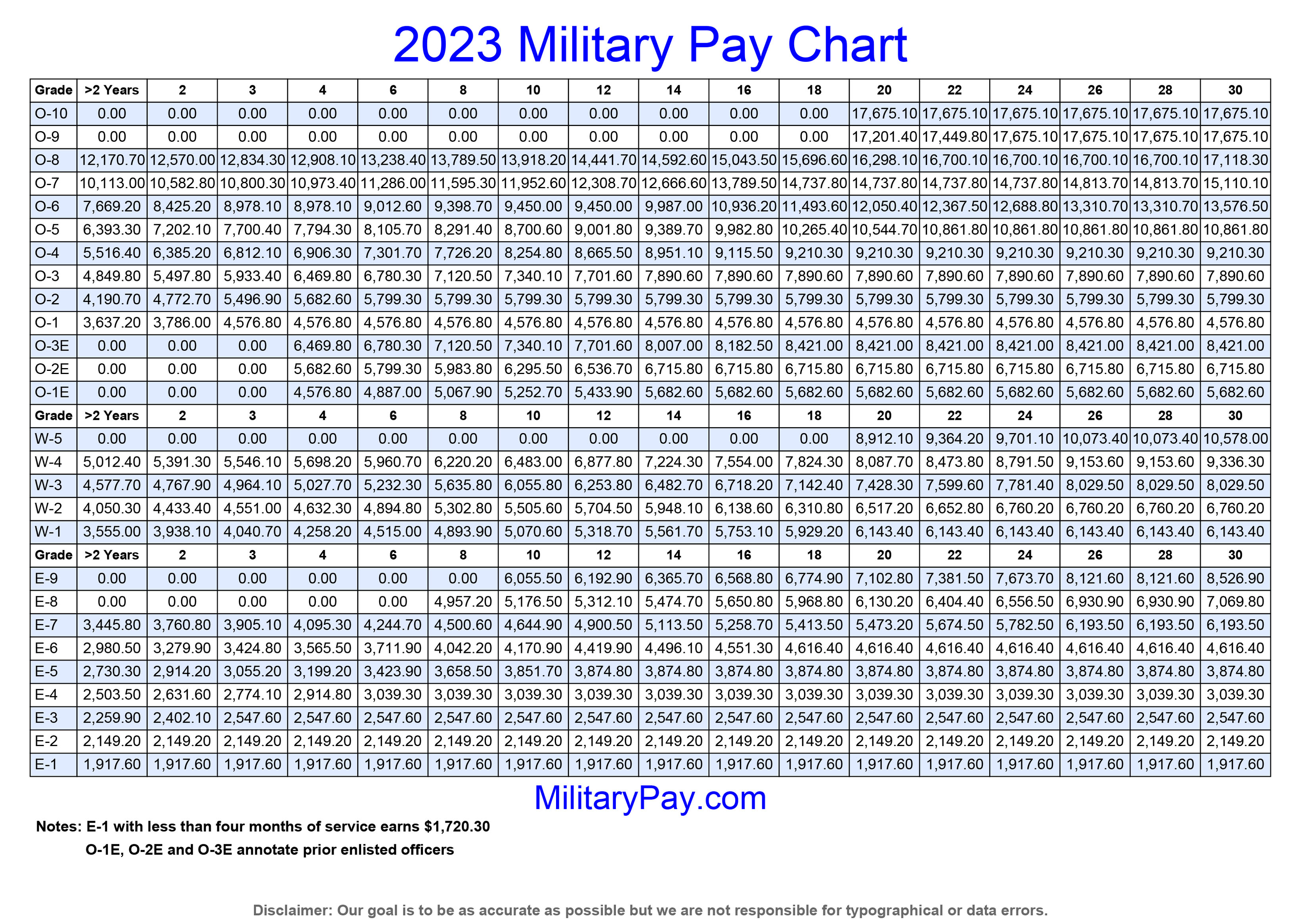
Source: militarypay.com
Beyond base pay, several special pays and allowances significantly impact total compensation. These include flight pay for aircrew members, hazardous duty pay for those in high-risk environments, and various other incentives. Housing allowances vary based on location and rank, offsetting the cost of living.
Examples of Total Compensation Calculation
For instance, a Staff Sergeant (E-5) with four years of service might receive a base pay of approximately $3,500 per month. Adding a housing allowance of $1,500 and flight pay of $300 brings their total monthly compensation to roughly $5,300. This is just an example, and actual figures vary considerably.
Factors Influencing Air Force Salary
Several key factors interact to determine an Air Force member’s salary. These factors are not independent but rather interconnected, creating a complex picture of compensation.
Years of Service, Rank, and Location
Years of service directly correlate with pay grade progression and thus salary increases. Higher ranks naturally command higher base pay. Location significantly influences housing allowances, with higher costs of living in major metropolitan areas resulting in higher allowances.
Understanding your worth is crucial, whether you’re navigating the Air Force NH pay scale or exploring other career paths. Our step-by-step guide helps you determine your deserved compensation within the Air Force. For those considering meteorology, researching potential earnings is equally important; check out this resource on chief meteorologist salary to see how compensation varies across fields.
Ultimately, knowing your value empowers you to negotiate fairly, whether in the military or the civilian sector.
Impact of Special Duties and Qualifications
Special duties or qualifications, such as specialized training or expertise in high-demand fields, often come with additional pay incentives. These bonuses can substantially increase overall earnings.
Comparison of Pay Scales Across Air Force Specialties
Pay scales can vary slightly between Air Force specialties, reflecting the demand for specific skills and experience. For example, highly technical specialties may offer higher base pay or greater opportunities for special pays.
Years of Service and Pay Grade Progression
| Years of Service | Enlisted Rank (Example) | Approximate Monthly Base Pay (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-2 | Airman Basic (E-1)
|
$2000 – $3000 | This is a broad range; actual pay varies. |
| 2-4 | Senior Airman (E-4)
|
$3000 – $4000 | This is a broad range; actual pay varies. |
| 4-6 | Technical Sergeant (E-6)
|
$4000 – $6000 | This is a broad range; actual pay varies. |
| 6+ | Senior Master Sergeant (E-8) and above | $6000+ | This is a broad range; actual pay varies significantly. |
Note: These are approximate figures and do not include allowances or special pays. Actual pay varies based on specific rank, years of service, and other factors.
Calculating Your Potential Earnings
Calculating potential Air Force earnings requires a systematic approach, considering various components of compensation.
Step-by-Step Earnings Calculation
- Determine Base Pay: Use official Air Force pay charts to find the base pay for your target rank and years of service.
- Identify Applicable Allowances: Consider housing allowances based on your assigned location and basic needs allowance (BAH) rates.
- Calculate Special Pays: Determine eligibility for flight pay, hazardous duty pay, or other special pays.
- Sum Components: Add base pay, allowances, and special pays to arrive at your total estimated monthly compensation.
Sample Calculation
Let’s say an Airman First Class (E-3) with two years of service is stationed at a location with a BAH of $1200. Their base pay is approximately $2500. Their total estimated monthly income would be $3700 ($2500 + $1200).
Resources for Determining Pay
The official Air Force pay charts and the MyPay system are the primary resources for determining current pay rates and accessing individual pay information.
Comparing Air Force Pay to Civilian Jobs
Comparing Air Force compensation to civilian jobs necessitates a holistic view, considering both salary and benefits.
Air Force Pay vs. Civilian Counterparts
A comparison should focus on jobs requiring similar skills and experience. For example, an Air Force pilot’s compensation can be compared to that of a commercial airline pilot, considering base pay, flight hours, benefits, and retirement plans.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Military vs. Civilian Careers
Military careers offer stability, benefits like healthcare and retirement, and opportunities for professional development. However, civilian jobs may offer higher potential earnings in some cases, and more flexibility in career paths.
Factors Beyond Base Pay
Healthcare, retirement plans, and educational opportunities are crucial benefits to consider when comparing overall compensation packages. The Air Force provides comprehensive healthcare and a generous retirement plan.
Examples of Civilian Job Comparisons
An Air Force engineer’s salary might be compared to that of a civilian engineer working for a defense contractor. Similarly, an Air Force medical professional’s compensation could be compared to that of a civilian doctor or nurse in a private practice or hospital setting. Salary ranges for these civilian jobs would need to be researched from reliable sources.
Advancement and Pay Progression
Career progression in the Air Force directly influences pay. Opportunities for advancement are plentiful, with corresponding salary increases.
Typical Career Progression and Pay Impact
A typical career path might involve starting as an Airman Basic (E-1) and progressing through the enlisted ranks (E-2 to E-9) or the officer ranks (O-1 to O-10). Each promotion results in a significant increase in base pay and potential for additional allowances and special pays.
Professional Development and Salary
Professional development opportunities, such as specialized training and further education, enhance an Airman’s skills and often lead to higher-paying positions or increased special pays.
Promotions and Pay Increases
Promotions are based on performance, experience, and availability of positions. Each promotion brings a substantial increase in base pay, making career progression a significant factor in long-term earnings.
Visual Representation of Career Path and Salary Growth
Imagine a graph with years of service on the x-axis and annual salary on the y-axis. The line would generally show an upward trend, with steeper increases at promotion points. The line would not be perfectly linear, as special pays and allowances can fluctuate.
Additional Compensation and Benefits: Get Paid What You Deserve A Step By Step Guide To The Air Force Nh Pay Scale
Beyond base pay, the Air Force offers a comprehensive package of additional compensation and benefits that significantly enhance the overall value proposition.
Additional Compensation and Benefits
- Bonuses: Various bonuses are available, depending on specialty, location, or performance.
- Retirement Plan: The Air Force offers a generous retirement plan, contributing a significant portion of an Airman’s retirement savings.
- Healthcare: Comprehensive healthcare coverage is provided for Airmen and their families.
- Life Insurance: Group life insurance is included as part of the benefits package.
- Education Assistance: Opportunities for tuition assistance and educational benefits are available.
- Commissaries and Exchanges: Access to discounted groceries and retail goods.
Air Force Retirement System, Get paid what you deserve a step by step guide to the air force nh pay scale
The Air Force retirement system is a defined benefit plan, providing a monthly retirement income based on years of service and rank. This system offers financial security for Airmen after their service concludes.
Value of Benefits in the Overall Compensation Package
The value of these additional benefits is substantial, significantly enhancing the overall compensation package beyond just base pay. These benefits contribute to a high quality of life and financial stability for Air Force personnel.
Closing Notes
Navigating the Air Force pay system can be challenging, but understanding the factors that influence your salary is crucial for career planning. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to calculating potential earnings and comparing them to civilian job equivalents. By understanding your potential earning power, along with the comprehensive benefits package offered by the Air Force, you can confidently assess the value of a military career and make informed decisions about your future.
